Attention A T users. To access the menus on this page please perform the following steps.
1. Please switch auto forms mode to off.
2. Hit enter to expand a main menu option (Health, Benefits, etc).
3. To enter and activate the submenu links, hit the down arrow.
You will now be able to tab or arrow up or down through the submenu options to access/activate the submenu links.
Locator
Contact
Search
VA »
Health Care »
National Center for Rehabilitative Auditory Research (NCRAR)
»
About Central Auditory Processing Disorders (CAPD)
National Center for Rehabilitative Auditory Research (NCRAR)
About Central Auditory Processing Disorders (CAPD)
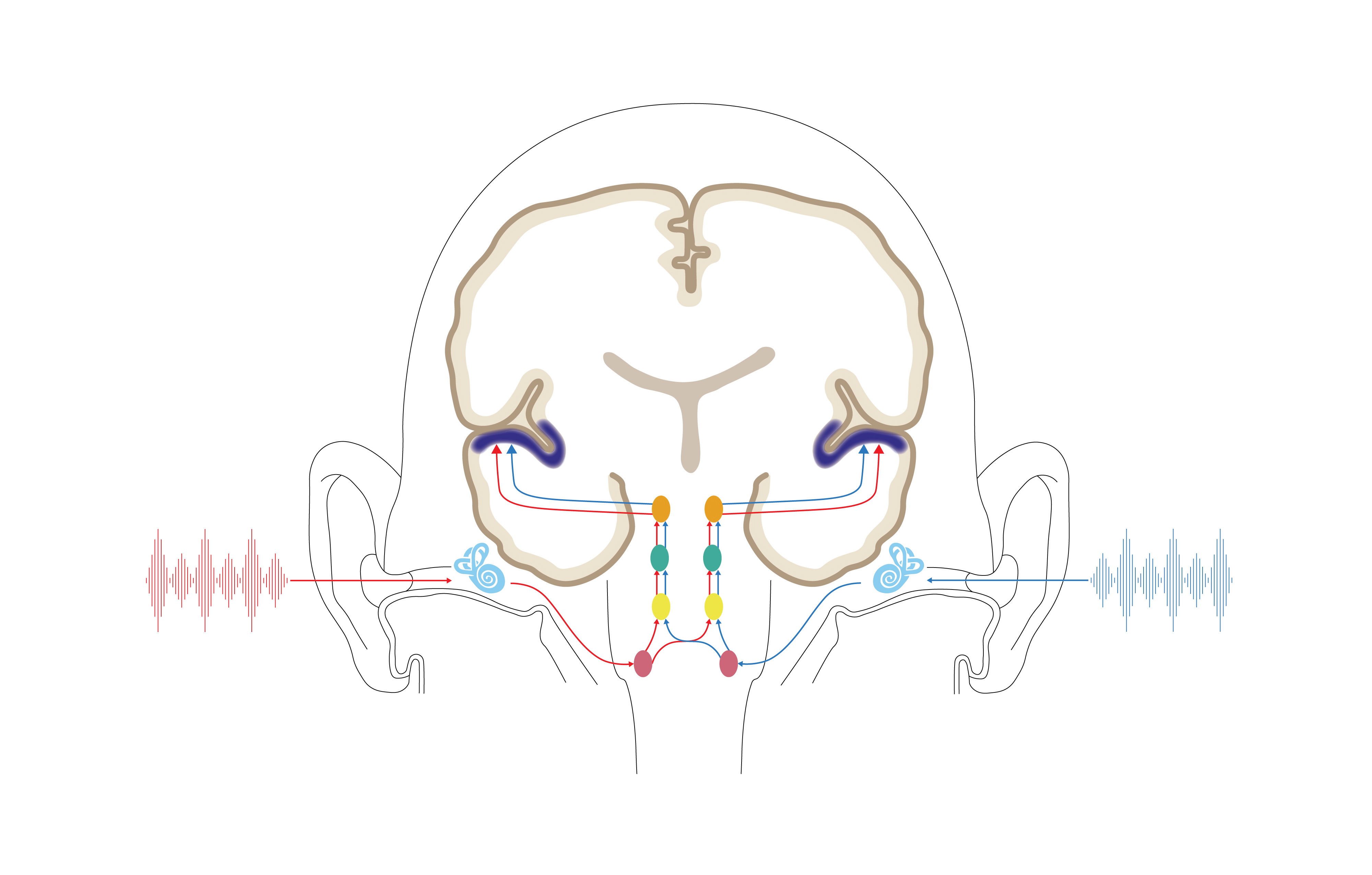 Sound signals travel from the ear through subcortical structures to the auditory cortex. Auditory processing disorder can be defined as “a condition in which people have trouble making sense of the sounds around them.” (National Institutes of Health) The sounds you hear travel from your ears, to and throughout your brain. Changes at any point along this pathway can interfere with how you process and understand the sounds you hear. Possible symptoms include:
Sound signals travel from the ear through subcortical structures to the auditory cortex. Auditory processing disorder can be defined as “a condition in which people have trouble making sense of the sounds around them.” (National Institutes of Health) The sounds you hear travel from your ears, to and throughout your brain. Changes at any point along this pathway can interfere with how you process and understand the sounds you hear. Possible symptoms include: - Struggling to recognize or understand speech in noisy settings
- Problems recognizing spoken words or keeping up with telephone conversations
- Finding it hard to tell the difference between words that sound alike
- Feeling uncertain about where the sounds you hear are coming from
Auditory processing difficulties can occur with other hearing problems, but auditory processing disorder is not the same as hearing loss. Testing can help to determine if symptoms are related to auditory processing disorder or not.
The terms CAPD (central auditory processing disorder) and APD (auditory processing disorder) are often used interchangeably. APD is sometimes preferred to describe auditory processing dysfunction that may involve peripheral and/or cognitive contributors. Research has shown that peripheral hearing structures can also be damaged without causing clinically observable hearing loss.
For more details, download this APD fact sheet.
Return to main menu.



















